What is Android Debug Bridge (ADB)?
- Adb Change Device Language
- Adb Change Devices
- Adb Change Device Settings
- Adb Shell Change Device Id
- Adb Change Device Name
Android Debug Bridge (ADB) is a command-line tool that allows you to communicate with a device. It is used to bridge communication between an emulator instance (Android device) and the background running daemon process (server). It helps you perform different actions like installing or debugging a device and run various commands on a device by providing access to a Unix shell.
Using any real device for mobile automation Testing has always been a challenge for testers. But, Android offers a handful of solutions to connect a real device over USB (Universal Serial Bus), i.e., Android Debug Bridge (ADB).
In this tutorial, you will learn-
This can be done either via button combination which differs from device to device or the easy method over adb command. Adb reboot fastboot Step 2. Fastboot oem writeimei 12347 Step 3. Verify that the IMEI has changed successfully run: fastboot getvar imei. Which should show the actual IMEI of the device. Change Screen Resolution on Android Method 1: Without Root. In this method, we will use Android Debug Bridge (ADB) to connect your device to a computer and issue commands to it. ADB is a command-line tool that lets you communicate with your device and is used for various actions like installing and debugging applications, changing resolution, etc. You can set the Device as owner from Android Studio. First go to the adb location which is at Platform-tools in Android Sdk and then run the adb shell command. I have give the full path and you can adjust at your requirement upon changing adb path and package name.
USB debugging and ADB Configuration-
APPIUM offers an advantage to execute test on real devices. But prior to run the test, we need to setup following pre-requisite.
- USB debugging should be enabled
- ADB configuration
- Desired capability setup as per the hardware changes.
Here we will see both, connecting to emulator as well as with real device for testing. See steps below for connecting to an emulator.
How to Connect to an Emulator
Pre-Requisite- SDK (Software Development Kit) should be installed on the machine. ADB in Android is packaged with Google's Android SDK (Software Development Kit). Steps to enable ADB from SDK Manager.

Step 1) Open Android SDK folder
Step 2) Double click on SDK Manager

Step 3) From the list of all packages select Tools and mark the checkbox for
- Android SDK Tools and
- Android SDK Platform-tools.
How to Connect Android Device with ADB (Android Debug Bridge)
Step 1) Enable USB Debugging on your device
Enable USB debugging option from 'Developer Option' in Android phone. Now, connect your Android device to the computer using USB cable.
Step 2) Go to the Android SDK folder
Open the local folder where Android SDK files has been saved 'Android SDK >> Platform-tools' eg: C:android-sdkplatform-tools
Step 3) Open the Command window
Inside folder hold Shift + Right click menu >> Select 'Open command window here' option.
It will open the folder using command prompt.
Note- you can also open the folder path directly from the Run command in command prompt.
This command window will directly open the folder in command prompt window.
Step 4) Connect an external Android device
Now, prior to check the device, user have to connect an external Android device (mobile phone). To connect use the device USB cable connector to the system. Then in above command prompt type command-
It will display all list of all the connected devices.
But, prior to this we should check that ADB server. Check whether it is running as background process or not. Just open the command prompt from above mentioned procedure and write 'adb' and press enter. It should display all the adb's process running.
When server starts, it always bind the local TCP port 5037. All ADB clients listen to 5037 TCP port to communicate with server request.

Now, the running ADB server can scan all connected emulator or device instances by scanning the port.
Always remember that ADB daemon runs on odd numbered port between the ranges of 5555 to 5558.
ADB daemon process runs with console connection that acquires even number port for connection.
For example: If single device connected then server automatically scan the device and get connected but if multiple device or emulator running the user need to give ADB connect to device USB command line instruction to connect.
The emulator instance connected on odd numbered port 5557 has the same console running over even numbered 5556 port ie. Each running devices has 1 odd and 1 even connected port.
Command to detect all connected device -
Command detecting a single device from multiple connected devices-
It will detect the adb connection for device -5554 and install the application.
So, this way user can set up a successful connection to access ADB USB connect instances using ADB commands.
Adb Change Device Language
How to Configuring ADB for Wi-Fi Support
Just like configuring ADB connect USB, user can also configure ADB over wi-fi.
Pre-requisite
- Both Android device and the host computer should be connected to same wireless network and
- Device Bluetooth option should disabled.
- Connect device using USB cable to the host computer. Confirm USB debugging is enabled in device.
- Set target device to connect TCP/IP on port 5555
Adb Change Devices
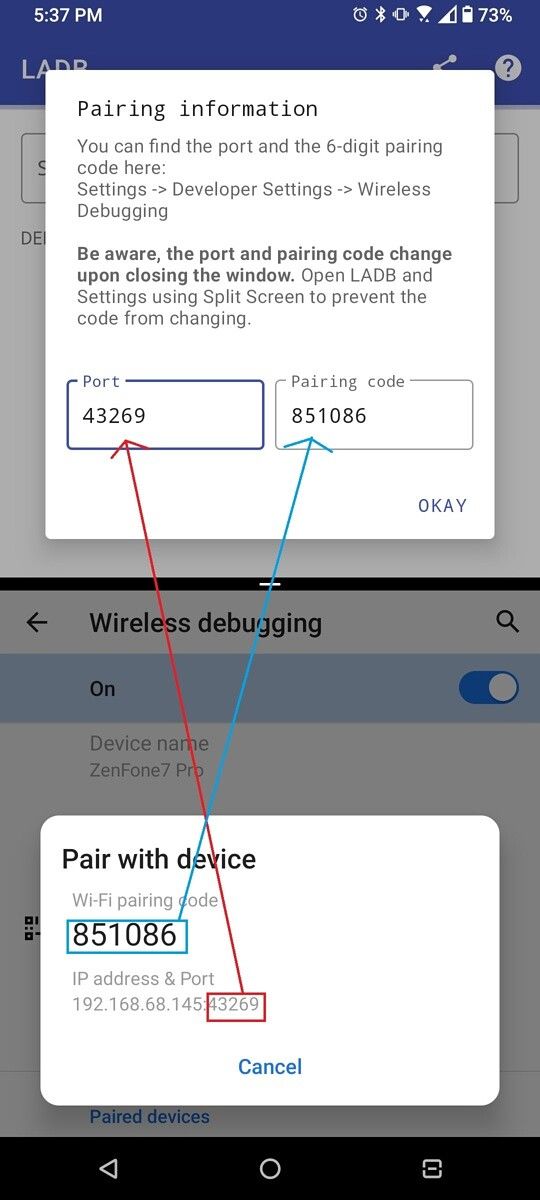
- Now, disconnect the USB cable from the device.
- In Android device find the IP address from Settings >> wi-fi Setting >> Advanced >> IP Address.
Use the same Android Debug Bridge IP address to connect the device via ADB connect device USB connection
Adb Change Device Settings
Hence, the final configuration done and 'adb' successfully configured over wireless network.
NOTE- If any connection error occurred just reset or kill the adb host connection. For that use following command
Adb Shell Change Device Id
<adb kill server> and again ADB connect to phone from first step.
Adb Change Device Name
The first step is to make sure you have the userspace governor available on your device..
root@:/ # cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_available_governors
interactive ondemand userspace powersave performance
we have the userspace governor on my Nexus 4, you should see it on any other Android device as well since it’s an old and simple governor.
Next we will set our governor to be userspace.
root@:/ # echo userspace > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor
root@:/ # cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor
usersapce
It is set now. If the governor isn’t set then scaling_governor will return something else.
Now it’s just a matter of determining what frequencies are available and setting them.
root@:/ cat /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_available_frequencies
384000 486000 594000 702000 810000 918000 1026000 1134000 1242000 1350000 1458000 1512000
For Locking CPU Frequecy at a particular level:
By using below mentioned ADB Command we can lock CPU Frequency
adb shell 'echo userspace > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_governor'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_max_freq'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu0/cpufreq/scaling_min_freq'
adb shell 'echo userspace > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu1/cpufreq/scaling_governor'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu1/cpufreq/scaling_max_freq'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu1/cpufreq/scaling_min_freq'
adb shell 'echo userspace > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu2/cpufreq/scaling_governor'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu2/cpufreq/scaling_max_freq'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu2/cpufreq/scaling_min_freq'
adb shell 'echo userspace > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu3/cpufreq/scaling_governor'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu3/cpufreq/scaling_max_freq'
adb shell 'echo 1600000 > /sys/devices/system/cpu/cpu3/cpufreq/scaling_min_freq'
If you are interested in how long your system spent in what state, check out the file